Stomach cancer – also known as gastric cancer – is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and is more common in the developing world.
Men are twice as likely as women to develop stomach cancer, and it is more common in older adults.
The stomach is part of the digestive system, located between the esophagus and the small intestine. It secretes enzymes and gastric acid to digest our food and produces a substance needed for vitamin B12 absorption. Our stomach also stores food, before muscular contractions send it to the small intestines.
Stomach cardia cancer occurs at the top part of the stomach closest to the esophagus, and stomach non-cardia cancer occurs in all other areas of the stomach.
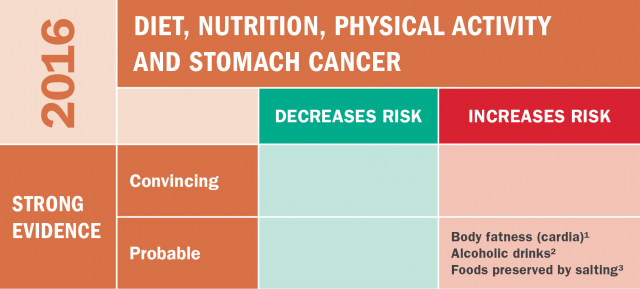
AICR’S latest report on stomach cancer found that maintaining a healthy weight can help lower cancer risk. High amounts of alcoholic drinks link to a higher risk of stomach cancer.
Lifestyle and stomach cancer risk.
- Weight
Excess body fatness puts you at greater risk for stomach cardia cancer.
- Obesity is characterized by a low-grade chronic inflammatory state. Such chronic inflammation can promote cancer development.
- Obesity promotes gastric reflux, possibly caused by elevated intra-abdominal pressure, which can promote the development of cancer.
- Obesity also promotes a precancerous condition called Barrett’s esophagus, which increases the risk of both cardia stomach cancer and esophageal cancer.
- Alcohol
Alcoholic drinks increase risk for all types of stomach cancer.
- Three or more alcoholic drinks (more than 1.5 ounces of pure alcohol) per day, increases risk.
- Acetaldehyde, the reactive metabolite of alcohol, is a recognized carcinogen.
- Alcohol also acts as a solvent, enhancing penetration of carcinogens into cells.
- Heavy consumers of alcohol may also have diets deficient in essential nutrients, rendering tissues more susceptible to carcinogenesis.
- Diet
Consuming foods preserved by salting is a probable cause of stomach cancer.
- Salt-preserved foods, such as meat and fish, and salt-preserved vegetables, especially when accompanied by H pylori bacteria, irritates the lining of the stomach over time in ways that make the cancer process more likely.
- Research mainly relates to high-salt foods and salt-preserved foods, including pickled vegetables and salted or dried fish, as traditionally prepared in East Asia.
- Other Factors
- Smoking: Smoking is a cause of stomach cancer.
- Infection: Helicobacter pylori infection is a cause of stomach non-cardia cancer.

Foods that fight stomach cancer.
No single food can protect you against cancer by itself. But research shows that a diet filled with a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans and other plant foods helps lower risk for many cancers.
Cancer Updates
The science of survival.
AICR’s health guides and recommendations are developed from research that focuses on how nutrition and lifestyle affect the prevention, treatment, and survival of cancer. Paramount to our updates is the Continuous Update Project which helps you stay on top of new findings, and understand the data that sits at the center of our work.