What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate Cancer is cancer that occurs in the prostate. Mutations appear in your cells and cause them to grow and amass rapidly, forming tumors. The prostate is a walnut sized gland in men that surrounds the top of the urethra just below the bladder outlet; it produces seminal fluid. Male hormones, such as testosterone, control its growth and function.
How Common is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide. Currently, 1 in 9 men will likely have prostate cancer in his lifetime. Diagnosis of the disease becomes more common as men age. In the US, about 60% of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men over age 65.
The vast majority of prostate cancers are diagnosed when the disease is confined to the prostate. In some cases, the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones and liver. This is called advanced prostate cancer. AICR’S latest report on prostate cancer found that maintaining a healthy weight is the best thing you can do to lower your risk of advanced prostate cancer.
Although it is unknown what causes prostate cancer specifically, the disease is tied to several risk factors.
What are the Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer?
- Weight
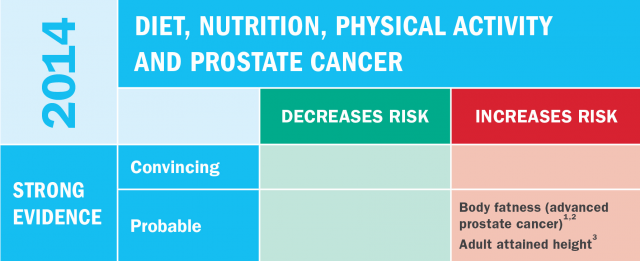
- There is strong evidence that having overweight or obesity increases the risk of advanced prostate cancer.
- Having obesity influences the levels of a number of hormones and growth factors. Insulin and leptin are elevated in people with obesity and can promote the growth of cancer cells.
- Sex steroid hormones, including estrogen, androgen, and progesterone, are likely to play a role in obesity and cancer. In men, having obesity is related to lower serum testosterone levels, which in turn may be associated with enhanced risk of or adverse outcome in advanced prostate cancer.
- Having obesity is characterized by a low-grade chronic inflammatory state. Such chronic inflammation can promote cancer development.
- Adult-attained height
- There is strong evidence that developmental factors in the womb, childhood, and adolescence that influence growth are linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
- Age
- The older you are, the greater the risk.
- Race/Ethnicity
- African American men are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer at a younger age, have the advanced form of the disease and die from prostate cancer compared to other men.
How Can You Lower Your Risk of Developing Prostate Cancer?
Monitor and maintain a healthy weight
Men who are obese, or have a high BMI, are more likely to have prostate cancer, so it’s important to keep an eye on your weight. If you are classed as overweight or obese, losing weight will help reduce your risk of prostate cancer. This can be achieved through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise.
For more information on what you can do to reduce your chances of developing cancer, check out our Cancer Prevention section.

Foods that fight cancer.
No single food can protect you against cancer by itself. But research shows that a diet filled with a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans and other plant foods helps lower risk for many cancers.
Cancer Updates
The science of survival.
AICR’s health guides and recommendations are developed from research that focuses on how nutrition and lifestyle affect the prevention, treatment, and survival of cancer. Paramount to our updates is the Continuous Update Project which helps you stay on top of new findings, and understand the data that sits at the center of our work.