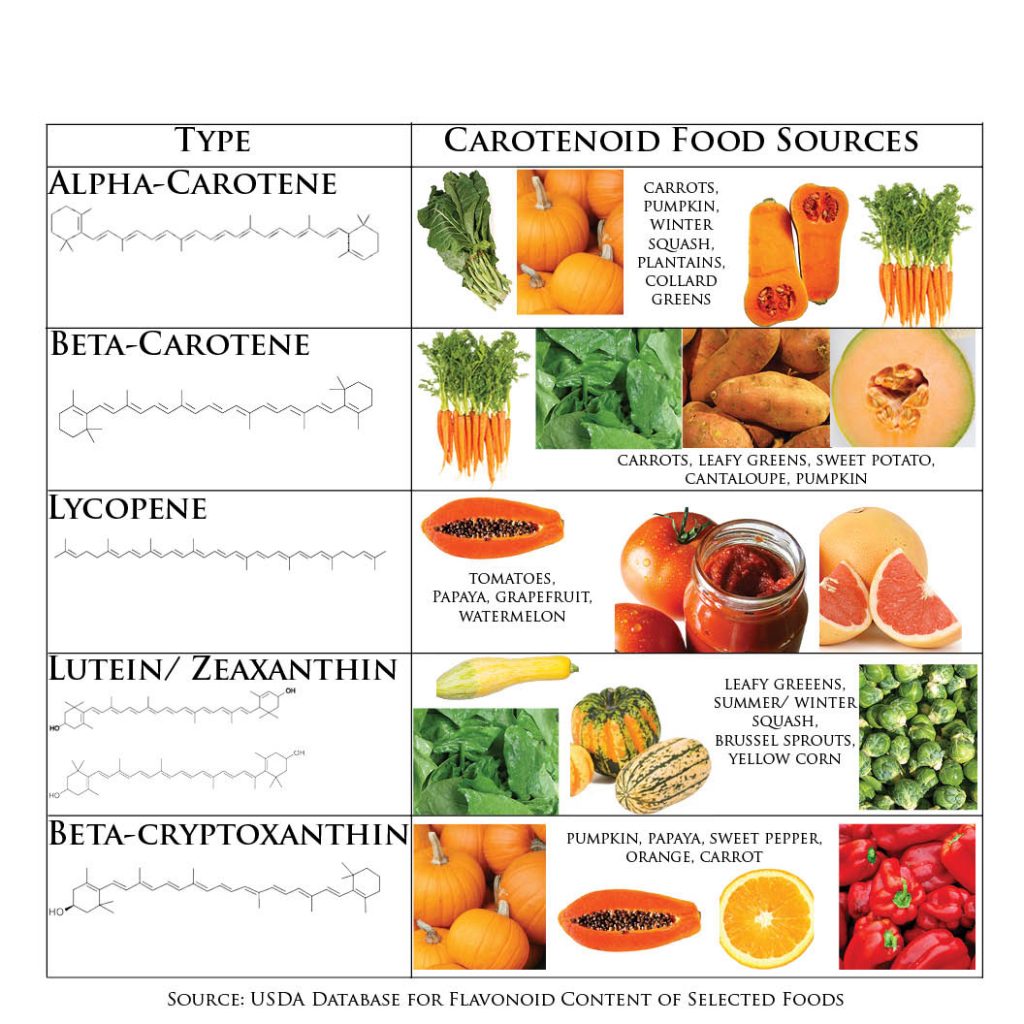
Looking for another reason to add carrots to your lunch or collard greens to dinner? Well, these are great sources of beta-carotene and alpha-carotene, types of carotenoids found in fruits and vegetables, And a new study suggests that women with higher blood concentrations of these carotenoids are at decreased risk of the type of breast cancer called estrogen receptor (ER) negative.
ER negative breast cancers do not have receptors for the hormone estrogen. These tumors are less common and often more difficult to treat than the more common ER-positive tumors that typically respond to estrogen.
 Recent studies, like this one, have linked carotenoids to decreased breast cancer risk.
Recent studies, like this one, have linked carotenoids to decreased breast cancer risk.
The new study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition included 1,502 women with breast cancer and 1,502 healthy controls from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) group.
Researchers chose to focus primarily on pre-menopausal and ER negative cancers because their review of the literature suggested that dietary carotenoids and fruit/ vegetable intake are more strongly related to these types of tumors.
Researchers compared prediagnostic blood levels of 6 carotenoids, including β-carotene and α-carotene as well as retinol, α-tocopherol, ϒ-tocopherol, and vitamin C for both groups. They took into account weight as well as other known risk factors for breast cancer.
Risk of ER negative breast cancer was 59 percent and 39 percent lower in women who had the highest blood concentrations of β-carotene and α-carotene respectively, compared to those who had the lowest levels. ER positive breast cancer risk was not associated with carotenoids or other nutrients.
Carotenoids are a large group of phytochemicals found in fruits and vegetables. You can usually recognize them by the orange, red, and yellow colors they give to foods. Many green leafy vegetables are also great sources.
These results may be another reason to consume more foods with beta carotene and alpha carotene. Supplements are not associated with the same decreased risk. And β-carotene in high-dose supplements, especially in smokers, seems to increase lung cancer risk and mortality.
The authors note that other factors including genetics and lifestyle can affect plasma carotenoid levels and may have affected the study results.
This study, and others, will be included in AICR/WCRF’s upcoming continuous update project report on breast cancer prevention. AICR’s previous review of the literature did not find a convincing link between foods containing carotenoids and breast cancer risk. Fruits and vegetables containing carotenoids are part of a cancer-preventive diet. AICR estimates that one-third of US breast cancers can could be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, and avoiding alcohol.
This study was supported by: Wereld Kanker Onderzoek Fond; Europe Against Cancer Program of the European Commission; Deutsche Krebshilfe, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum; German Federal Ministry of Education and Research; Danish Cancer Society; Health Research Fund of the Spanish Ministry of Health, Spanish Regional Governments of Andalucia, Asturia, Basque Country, Murcia (No. 6236), and Navarra; Catalan Institute of Oncology, Red de Centros RCESP, C03/09, Spain; Cancer Research UK; Medical Research Council, United Kingdom; Stroke Association, United Kingdom; British Heart Foundation; Department of Health, United Kingdom; Food Standards Agency, United Kingdom; Wellcome Trust, United Kingdom; Helenic Health Foundation; Italian Association for Research on Cancer; Italian National Research Council, Fondazione-Istituto Banco, Napoli, Italy; Dutch Ministry of Public Health, Welfare and Sports; Dutch Prev ention Funds; LK Research Funds; Dutch ZON (Zorg Onderzoek Nederland); World Cancer Research Fund; Swedish Cancer Society; Swedish Scientific Council; Regional Government of Skane, Sweden; European Research Council; French League against Cancer; National Institute for Health and Medical Research, France; Mutuelle Généralede; Education Nationale, France; 3M Co, France; Gustave Roussy Institute, France; and General Councils of France.





Breast cancer – the real Elephant is definitively covered in “The No Dairy Breast Cancer Prevention Program” by eminent scientist prof. Jane Plant CBE. First notice that the Dairy regions of the world are exactly the Breast Cancer regions. Quick view Cow’s milk is expressly for growing calves into big cows as rapidly as possible. This includes natural IGF1 growth hormone which helps fast growing cells to grow faster. Human breast cancer cells thrive. Read the book, Amazon & booksellers.