Smoking cigarettes is the cause of an estimated 80-90 percent of lung cancer cases. AICR’s latest report evaluated how other lifestyle factors affect the risk of developing lung cancer.
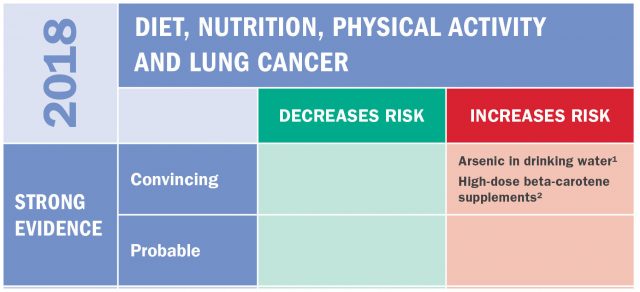
The Expert Report analyzed other lifestyle factors and their effect on lung cancer risk and found that arsenic in drinking water increases the risk of this cancer. Among smokers and former smokers, high-dose beta supplements also increase the risk. To reduce lung cancer risk, there was some evidence suggesting that physical activity and not drinking alcohol can lower the risk.
Lifestyle and lung cancer risk.
- Diet
There is strong evidence that drinking water containing arsenic increases the risk of lung cancer.
- Water can become contaminated by arsenic from natural deposits in the earth or from agricultural and industrial practices. In the US, public drinking water systems test for arsenic and are required to keep it below a specific level. Countries particularly affected by arsenic in drinking water include Bangladesh, India, Cambodia, Argentina, Chile and Mexico.
- Supplements
In current and former smokers there is strong evidence that taking high-doses of beta-carotene supplements increases the risk of lung cancer.
- The evidence comes from studies of current and former smokers taking daily supplements containing 20 milligrams for beta-carotene; 25,000 IU/day for retinol.
- Smoking and tobacco products
Smoking cigarettes is the primary cause of lung cancer.
- The risk of developing lung cancer is several times higher in heavy cigarette smokers. Smoking cigars, pipes and other tobacco products also increase the risk. Carcinogens in tobacco smoke and other inhaled particles can interact directly with the DNA of lung cells. The particles may also lead to chronic inflammation, which can play a role in the development of lung cancer.
- Previous lung disease
A history of emphysema, chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis or pneumonia is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.
- People with antibodies to Chlamydia pneumonia, a type of bacterium that can cause chest infections, have an increased risk of lung cancer.
- Occupational exposure
Exposure to asbestos, crystalline silica, radon and mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals are associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.
- Indoor air pollution
Pollution from wood and coal burning for cooking and heating increases the risk of lung cancer.

Foods that fight cancer.
No single food can protect you against cancer by itself. But research shows that a diet filled with a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans and other plant foods helps lower risk for many cancers.
Cancer Updates
The science of survival.
AICR’s health guides and recommendations are developed from research that focuses on how nutrition and lifestyle affect the prevention, treatment, and survival of cancer. Paramount to our updates is the Continuous Update Project which helps you stay on top of new findings, and understand the data that sits at the center of our work.